Bariatric surgery, also known as weight loss surgery, involves making changes to your digestive system to help an individual lose weight.
The procedure is performed on individuals who are obese or have severe obesity. They are typically recommended when diet and exercise haven’t worked or when you have serious health problems because of your weight.
Bariatric surgery aims to help individuals lose weight and improve their overall health and quality of life.
Bariatric surgery types
There are several different types of bariatric surgery, including gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y), sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding.
Each type of surgery works in a slightly different way, but all aim to help individuals lose weight by decreasing the amount of food they can eat or absorb.
Gastric bypass surgery
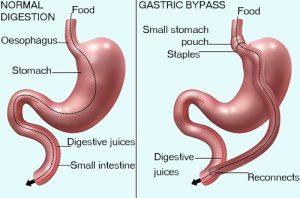
This is perhaps the most common type of bariatric surgery. During this procedure, the surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach and links it directly to the small intestine. This bypasses a large part of the stomach and small intestine. This ultimately reduces the amount of food the individual can eat and absorb.
Sleeve gastrectomy
It involves the surgeon removing a large portion of the stomach (about 80%), leaving behind a smaller, tube-like pouch. This smaller stomach can hold less food, which helps individuals feel full more quickly and eat less.
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch
According to Mayo Clinic, this is a two-part surgery. The first step involves performing a procedure similar to a sleeve gastrectomy. The second surgery involves connecting the end portion of the intestine to the duodenum near the stomach (duodenal switch and biliopancreatic diversion), bypassing the majority of the intestine.
This surgery serves to limit how much you can eat and also reduces the absorption of nutrients. While quite effective, biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch has greater risks, including malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies.
Adjustable gastric banding
This involves the surgeon placing an inflatable band around the upper part of the stomach. The band can be tightened or loosened to adjust the size of the opening between the two parts of the stomach. Adjustable gastric banding is a less common type of bariatric surgery that is known to make a person feel full faster and thus eat less.
Who it’s for
Bariatric surgery is usually only recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher.
What’s more, it can also be helpful for individuals with a BMI of 35 or higher and one or more serious health conditions related to obesity, such as type 2 diabetes or sleep apnea.
Bariatric surgery is a major procedure that carries risks and demands significant lifestyle changes. It is therefore only recommended where diet and exercise have failed to yield results.
Before deciding to undergo bariatric surgery, it’s important for individuals to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of the procedure.
It is also important to work closely with a healthcare team to determine if it is the right option.
This may include consultations with a surgeon, a dietitian, and a mental health professional, as well as a rigorous physical examination and evaluation of an individual’s overall health.
The good news is that bariatric surgery can lead to significant and sustained weight loss in addition to improvements in health conditions related to obesity, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
In many cases, these health conditions can be resolved or greatly improved following bariatric surgery.
It should be noted that bariatric surgery is not a quick fix or a magic wand for weight loss. It is a tool that can help individuals make lasting changes to their diet and lifestyle. Importantly, it requires a lifelong commitment to healthy habits.
Bariatric surgery risks
As with any surgery, bariatric surgery carries some risks that include:
Infection: An infection could occur at the surgical site or in the urinary tract, respiratory tract, or other areas of the body.
Blood clots: Blood clots can form in the legs or lungs after surgery, which can be serious or even life-threatening.
Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during or after surgery, which may require additional treatment.
Nutrient deficiencies: Bariatric surgery can lead to deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, and minerals, if an individual fails to follow a proper diet after the procedure.
Dumping syndrome: This occurs when food moves too quickly through the small intestine and can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Narrowing of the stomach pouch or opening: In some cases, the stomach pouch or opening created during bariatric surgery may narrow, which can cause food to become stuck and require additional treatment.
Death: As with any major surgery, there is a risk of death, although this is rare.
It’s important to meticulously weigh the risks of bariatric surgery and discuss them with healthcare professionals before making a decision about whether to undergo the procedure.
READ ALSO: Example of 7-Day Diet Chart for Weight Loss for Busy Woman
By the same token, it is also important for individuals to seek medical attention if they experience any concerning symptoms after the surgery.
Do you have a story you would like us to publish? Please reach us at info@gotta.news.






















